Program Topics

“Woodrow Wilson and America’s First Attempt at Establishing a New World Order”
America’s first effort at establishing a new world order on behalf of a troubled world was the vision President Woodrow Wilson put forth at the Versailles Peace Conference in the spring of 1919. Historians view this as a failed effort because the U.S. did not join the League of Nations after World War I. This presentation will contend that Wilson did succeed in fostering a new world in Europe that despite World War II and the Cold War is in place today. A Europe at peace with itself is the result.
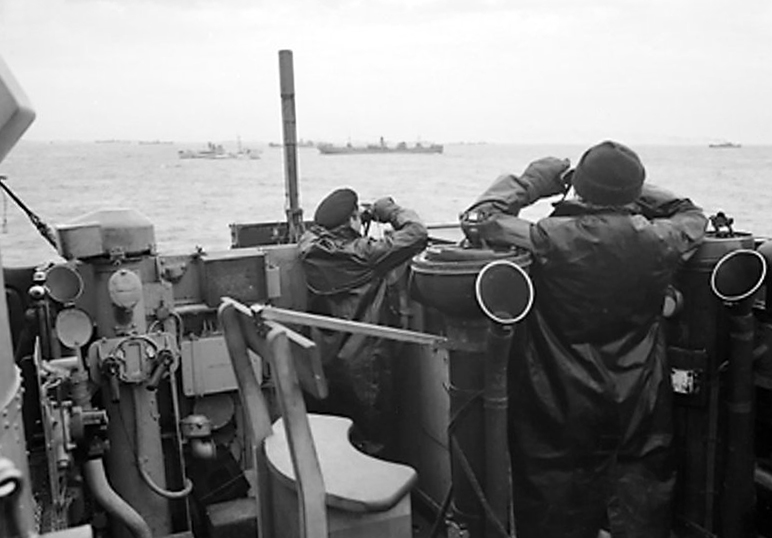

“BATTLE FOR THE ATLANTIC, DECEMBER 1941 – MAY 1943”
One of the crucial turning point battles of World War II which had to be won, the battle lasted over a year and a half. Dominating the Atlantic was Nazi Germany’s Kriegsmarine and its U-boat wolfpacks until the Allies adopted critical methods to countering them all. Come and hear all about this important battle which upon attaining victory, enables the Allies to conduct Operation Overlord, the invasion of North West France on June 6, 1944.

“THE TEHRAN CONFERENCE, NOVEMBER 1943:
FIRST MEETING OF THE BIG THREE”
The Allies’ Tehran Conference, codenamed EUREKA, was held November 28 to December 1, 1943. It was the first meeting of the Big Three: British Prime Minister Winston Churchill; U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt; and Soviet Union Premier Joseph Stalin. At this critical meeting, key directions were decided upon which led to the Allies to victory over Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan.This presentation relates what the key decisions were, why they were made and
their overall impact on the outcome of WW II.

“BATTLE FOR BATAAN: WHEN MEN HAVE TO DIE”
The Bataan peninsula, a strip of land 25 miles long and 20 miles wide, on the Philippine Island of Luzon became the last refuge for the troops defending the island against a Japanese invasion, December 1941. Over 67,500 Filipino soldiers and 12,500 US service personnel starved of adequate food and supplies rendered a desperate yet hopeless defense ultimately surrendering on April 9, 1942. Some 78,000 men were then herded out of the peninsula in what became known as the brutal Bataan Death March. The presentation will cover all aspects of the 4 month long battle and its impact on the history of WW II.

“WORLD WAR II TURNING POINTS: CRITICAL BATTLES THAT ENABLED THE ALLIES TO GO ON THE OFFENSE”
A turning point is a point in a war or campaign where one combatant experiences a reversal in fortune. The combatant losses the initiative, suffers loss of freedom in a theater of war and the opponent assumes the offensive. In WW II there were five key turning point battles each of which enabled the Allies to mount offensive operations to achieve strategic objectives and ultimately attain victory. The presentation will relate what the five critical battles were and their outcomes.

“BATTLE FOR GUADALCANAL, AUGUST 1942”
Guadalcanal, a Japanese occupied island in the Solomon Island chain in the South Pacific was invaded by a major US Marine force on August 7, 1942. The bloody and protracted struggle for this steamy, malaria-ridden, rain-sodden island lasted for nearly 6 months resulting in over 6000 casualties to include 1752 battle deaths. The battle was the first real test of land strength between Japan and the USA. Seven major naval battles were also fought around the island. Guadalcanal is now seen as a major turning point in the Pacific war from which Japan never recovered. Come and hear why the battle was so vicious and why it had to be won.
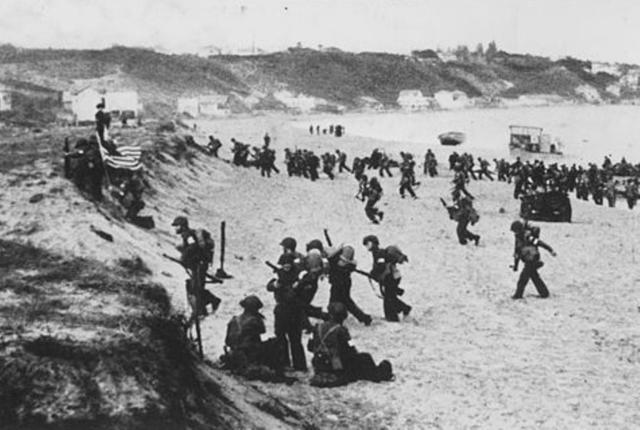

“OPERATION TORCH: ALLIED INVASION – NORTH AFRICA”
On November 8, 1942 an Anglo-American force landed in French Morocco and Algeria with the aim and goal to gain complete control of North Africa and defeat General Erwin Rommel’s German-Italian Army in Libya. TORCH was primarily an American operation under the command of Lt.-General Dwight D. Eisenhower assisted by a British staff. The presentation will relate all aspects of this first successful Allied combined operation and how and why it did succeed.
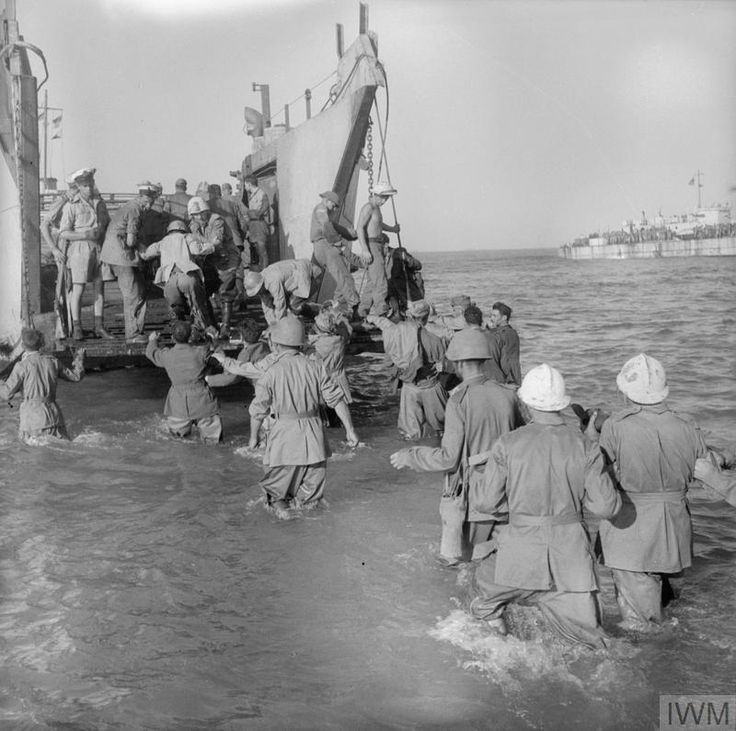

“OPERATION HUSKY AND THE COLLAPSE OF FASCIST ITALY”
The decision to invade Sicily codenamed Operation Husky as part of the Allies’strategy to win the battle for the Mediterranean was made at the Casablanca Conference in January 1943. The planning stage of this combined forces operation was confused and protracted and the operation, conducted on July 10, 1943, hardly less so. However once on shore encountering experienced German and Italian military units, the American army came of age as a fighting force. Military victory was attained on August 16 and surprisingly, the victory caused the downfall of the Fascist government in Italy. The presentation will cover the important aspects of this combined operation and their impact.

“A Failure in American Diplomacy: Summer 1941”
War with Japan could have been avoided in 1941. Although many historians state that war in the Pacific was inevitable, a window of opportunity to resolve issues diplomatically did present itself in the summer of 1941. The presentation will cover what the failure in American diplomacy was all about and most importantly, why.

“Operation Barbarossa: The Invasion of the USSR by Nazi Germany”
On June 22, 1941, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union using the largest armed force ever assembled. More than 3 million troops, 600,000 vehicles, 750,000 horses, 3,580 tanks, and 1,830 were hurled against the Russians who were caught totally unprepared. The presentation will cover all aspects of the massive assault and why Premier Joseph Stalin was surprised by the attack. Stalin had been warned many times about the planned invasion.

“World War II – The 20th Century’s Most Significant Event”
A presentation on the history of the World War II Era and its impact on world history. WW II was the most violent and devastating war ever fought with nearly 60 million lives lost due to battle, aerial bombing, acts of genocide and the use of atomic bombs.
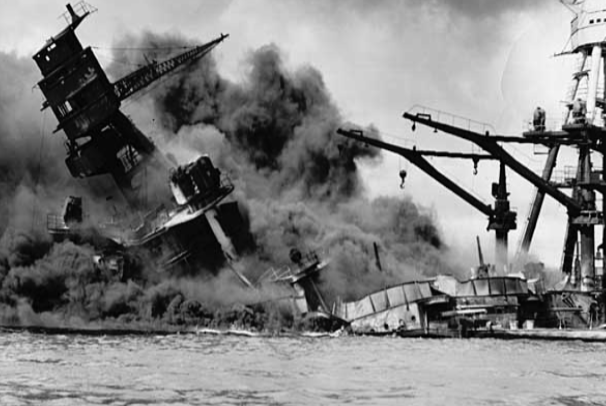

“Pearl Harbor: A Day Of Infamy”
Early in the morning of December 7, 1941, Japanese carrier-based planes and submarines attacked the U.S. Pacific Fleet and nearby military airfields at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Eight American battleships and ten other naval vessels were sunk or badly damaged. A total of 64 American aircraft were destroyed and over 3,400 military personnel were killed or wounded. The attack marked the entrance of Japan into World War II on the side of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy and the entrance of the U.S. on the side of the allies – thus World War II. The attack was always considered possible but not probable. Were critical judgment errors made by America’s national leaders and its military that made America so vulnerable or did motivations by America’s European allies to have America represented in WW II result in this devastating attack? Listen to this stimulating presentation to find out.
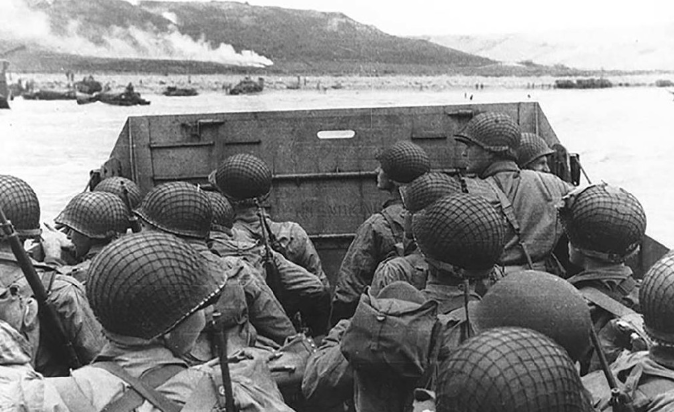

“D-Day June 6, 1944 – Why Did It Succeed?”
Operation Overlord, the amphibious invasion of north west France on June 6, 1944, the largest seaborne assault ever conducted, was carefully planned over a six month period as a combined, joint service operation. The operation nearly failed. This presentation will review the details of this crucial invasion.

“THE STRATEGY TO DEFEAT IMPERIAL JAPAN”
Presentation relates the complex strategy to defeat Imperial Japan as determined right after Japan attacked America on 7 December 1941. The strategy was determined at the Arcadia Conference held in Washington, D.C. right after Pearl Harbor, a critical conference at which all the key American and British military leaders were present. The strategy was primarily determined by America’s military chiefs because the war in the Pacific was going to be mostly an American effort. The initiation of that effort was no easy undertaking for a nation that was totally unprepared for war prior to the attack on Pearl Harbor. In other words, the defeat of Imperial Japan just did not happen. Come and hear how, when, and why.

“BATTLE OF THE BULGE, DEC. 1944: GREATEST AMERICAN BATTLE”
The Battle of the Bulge, Adolf Hitler’s final counter offensive in northwest Europe, was launched on December 16, 1944. Aimed at splitting the Allied armies in half and capturing the key port of Antwerp, the offensive surprised the Allies and caused an immediate command crisis. The presentation will cover how the crisis was overcome, how the offensive was thwarted and why the battle was called by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill the “greatest American battle of the war.
[custom_frame_lef

“WITNESSING HISTORY – UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER, MAY 1945”
Enunciated by President Franklin Roosevelt at the Casablanca Conference, January 1943, the policy of “unconditional surrender” brings about the total defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945. On May 7, 1945, at Supreme Allied Commander General Dwight D. Eisenhower’s headquarters in Rheims, France, the German high command signed an unconditional surrender document. Present to take photos at the signing was Technical Sergeant Al Meserlin, General Eisenhower’s wartime photographer. This presentation detail the circumstances leading up to the signing and enable you to actually witness history via the photos Sgt. Meserlin took of the historic event. Victory in Europe (VE) Day was officially declared the next day.

“VICTORY OVER JAPAN (VJ) DAY – IT JUST DIDN’T HAPPEN”
VJ Day, 15 August 1945, was the day victory over Japan was celebrated throughout Allied countries. Japan formally announced that it had accepted Allied terms for “unconditional surrender” the day before. The date the Japanese signed the actual surrender document, 2 September 1945, also became known as VJ Day. The presentation will detail how eventual victory over Japan was achieved in the summer of 1945 and the methods used to do so.
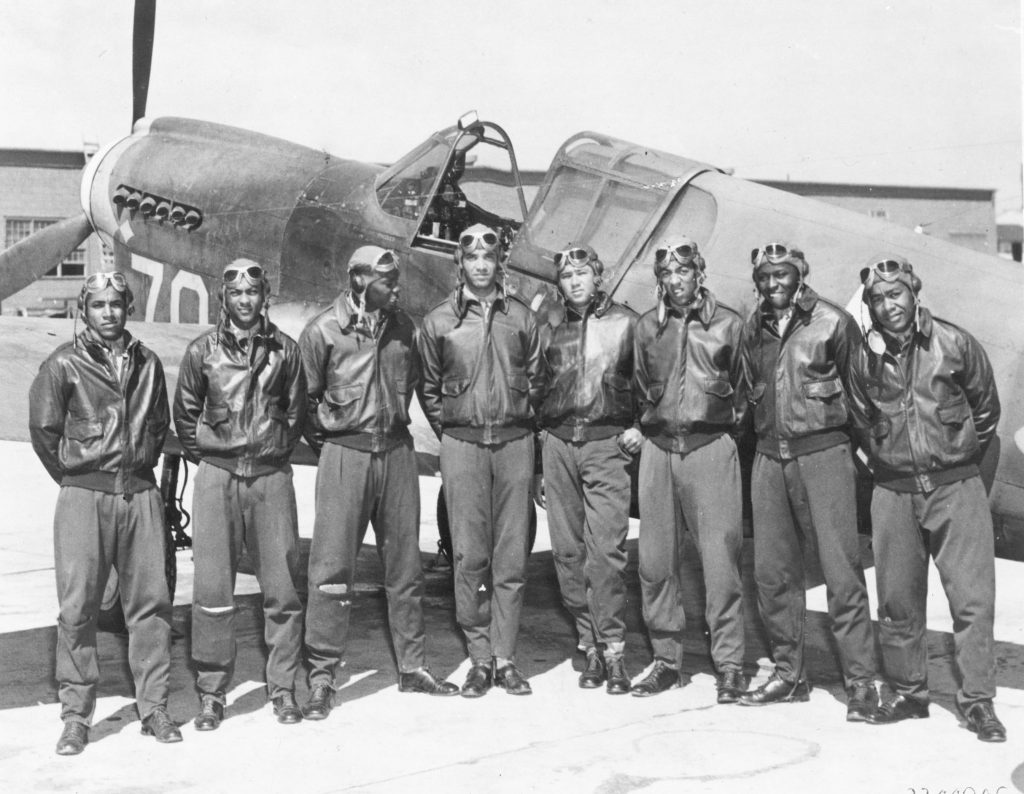

THE TUSKEGEE AIRMEN – AMERICA’S FIRST BLACK PILOTS
The Tuskegee Airmen were a group of primarily
Africa-American military pilots and airmen who fought in World War II. They were the first African-American military
aviators in the U.S. armed forces. Trained
on five airfields surrounding Tuskegee University in Alabama, their training
was the first de-segregated training to take place within a segregated U.S.
military. It became the first dramatic move
forward to racial and social equality within America. The presentation will cover the history of
the formation of the Tuskegee Airmen, the unit’s wartime accomplishments and
the unit’s overall effect on American society

THE KOREAN CONFLICT: AMERICA’S FORGOTTEN WAR
The Korean Conflict has been called America’s “forgotten war” but it had a profound impact upon East-West relations during the Cold War. More than 54,000 Americans died attempting to halt the spread of Communism through South Korea. On June 25, 1950 over 90,000 North Korean troops trained and equipped by the Soviet Union poured over the 38th Parallel and invaded South Korea resulting in three years of brutal conflict. Learn via this presentation about the aspects of the war and the Armistice that brought it to a halt, an armistice still in place today.
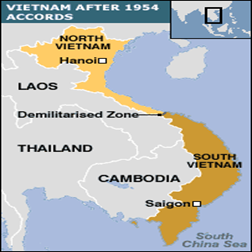
THE VIETNAM WAR, 1956 – 1975: HOW IT ALL BEGAN
The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos. and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon, capitol of South Vietnam, on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. North Vietnam was supported by the Soviet Union, China and other communist allies. South Vietnam was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The presentation will address how it all began.

THE VIETNAM WAR, 1964 – 1973
The Vietnam War was a long, costly and divisive conflict that pitted the communist government of North Vietnam against South Vietnam and its principal ally, the United States. The conflict was intensified by the ongoing Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union. More than 3 million people (including over 58,000 Americans) were killed in the Vietnam War, and more than half of the dead were Vietnamese civilians. Via the presentation, come to learn where the war was fought, how it was fought and most importantly, why it was fought.



